 Precision electronic medicine in the brain
Precision electronic medicine in the brainAbstract
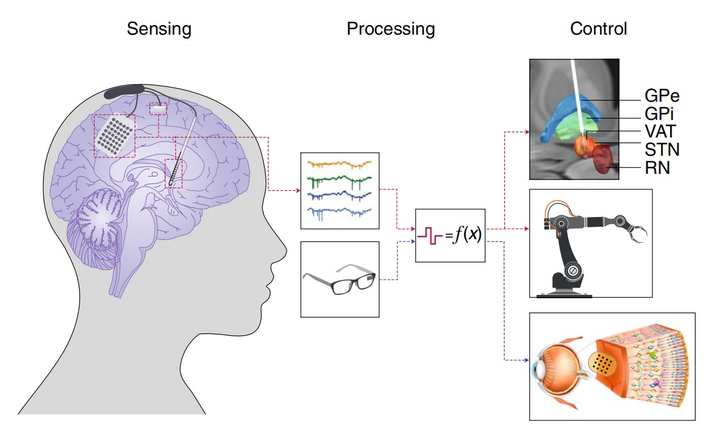
This perspective article explores the emerging field of precision electronic medicine in the brain, highlighting how advanced neural interface technologies are enabling personalized therapeutic approaches for neurological and psychiatric disorders. The work discusses the convergence of electronics, neuroscience, and medicine to create targeted, patient-specific treatments that can adapt to individual brain dynamics and pathophysiology. Key topics include closed-loop neurostimulation systems, biocompatible neural interfaces, and the potential for real-time monitoring and modulation of brain activity.
This influential perspective article published in Nature Biotechnology presents a comprehensive vision for precision electronic medicine in the brain, exploring how cutting-edge neural interface technologies are revolutionizing the treatment of neurological and psychiatric disorders.
Key Concepts
- Precision Medicine Approach: Tailoring electronic therapies to individual patient characteristics and brain dynamics
- Closed-Loop Systems: Real-time monitoring and adaptive stimulation based on neural feedback
- Biocompatible Interfaces: Advanced materials and designs for long-term brain integration
- Personalized Therapeutics: Patient-specific treatment protocols based on individual pathophysiology
Technological Foundations
The article discusses several breakthrough technologies:
- Advanced Neural Interfaces: Next-generation electrodes and recording systems for high-fidelity brain monitoring
- Adaptive Algorithms: Machine learning approaches for real-time therapy optimization
- Wireless Systems: Untethered devices for continuous monitoring and treatment
- Biointegrated Electronics: Tissue-like electronic systems that seamlessly interface with neural tissue
Clinical Applications
The precision electronic medicine approach has transformative potential for:
- Epilepsy Treatment: Personalized seizure prediction and prevention systems
- Depression and Psychiatric Disorders: Adaptive deep brain stimulation based on mood biomarkers
- Movement Disorders: Closed-loop systems for Parkinson’s disease and essential tremor
- Chronic Pain Management: Targeted spinal cord and peripheral nerve stimulation
- Brain-Computer Interfaces: Personalized neural prosthetics for paralyzed patients
Future Directions
The article identifies key areas for advancement:
- Biomarker Discovery: Identifying reliable neural signatures for different conditions
- Algorithm Development: Creating robust, adaptive control systems for therapeutic devices
- Regulatory Pathways: Establishing frameworks for personalized electronic medicine devices
- Clinical Translation: Moving from research prototypes to clinical practice
Challenges and Opportunities
Key considerations include:
- Safety and Efficacy: Ensuring long-term safety of implanted electronic systems
- Scalability: Developing cost-effective manufacturing for widespread adoption
- Data Privacy: Protecting sensitive neural data in connected medical devices
- Interdisciplinary Collaboration: Integrating expertise from engineering, neuroscience, and medicine
Significance
Published in Nature Biotechnology (Impact Factor: ~54), this perspective article provides a roadmap for the future of brain medicine. The authors envision a paradigm shift from one-size-fits-all treatments to personalized, adaptive therapies that can respond to individual patient needs in real-time.
The work highlights the potential for electronic medicine to transform neurological and psychiatric care, offering hope for millions of patients with currently intractable conditions. By combining advanced materials science, sophisticated algorithms, and deep understanding of brain function, precision electronic medicine represents the next frontier in neurotechnology.