 Novel electrode technologies for neural recordings
Novel electrode technologies for neural recordingsAbstract
This comprehensive review examines the latest advances in electrode technologies for neural recordings, covering both conventional and emerging approaches. The article discusses the evolution from traditional metal electrodes to sophisticated nanoscale devices, highlighting innovations in materials science, fabrication techniques, and biointegration strategies. Key topics include flexible electronics, mesh-like neural interfaces, and biocompatible materials that enable long-term, high-fidelity neural recordings with minimal tissue damage.
This influential review article published in Nature Reviews Neuroscience provides a comprehensive overview of the rapidly evolving field of neural electrode technologies, examining both established methods and cutting-edge innovations that are transforming neuroscience research and clinical applications.
Key Topics Covered
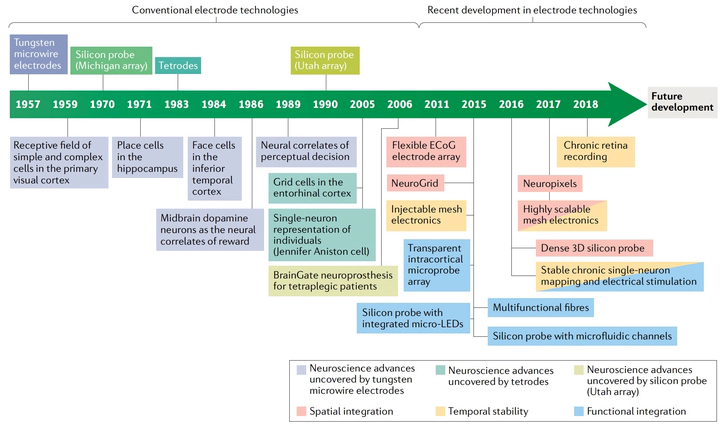
- Traditional Electrode Technologies: Historical development and current applications of conventional metal electrodes
- Flexible Electronics: Revolutionary approaches using bendable and stretchable materials for better biointegration
- Nanoscale Interfaces: Ultra-small electrodes enabling single-neuron resolution recordings
- Biocompatible Materials: Advanced materials that minimize immune responses and tissue damage
- Fabrication Techniques: State-of-the-art manufacturing methods for next-generation neural interfaces
Technological Innovations
The review highlights several breakthrough technologies:
- Mesh Electronics: Ultra-flexible, tissue-like electronic networks that seamlessly integrate with neural tissue
- Organic Electronics: Biocompatible organic materials for improved long-term stability
- Wireless Systems: Untethered recording systems for freely behaving animal studies
- High-Density Arrays: Massively parallel recording capabilities for large-scale neural monitoring
Clinical and Research Applications
The technologies discussed have broad implications for:
- Brain-Computer Interfaces: Next-generation neural prosthetics and assistive devices
- Neurological Disease Treatment: Advanced monitoring and therapeutic interventions
- Fundamental Neuroscience: Understanding brain circuits and neural computation
- Drug Development: Real-time assessment of neural responses to therapeutic compounds
Future Directions
The review identifies key challenges and opportunities:
- Long-term Biointegration: Developing truly chronic, stable neural interfaces
- Scalability: Manufacturing techniques for widespread clinical adoption
- Signal Processing: Advanced algorithms for extracting meaningful information from complex neural data
- Closed-loop Systems: Real-time feedback systems for therapeutic applications
Significance
Published in Nature Reviews Neuroscience (Impact Factor: ~38), this comprehensive review serves as an essential reference for researchers, engineers, and clinicians working in neurotechnology. The article bridges materials science, bioengineering, and neuroscience, providing insights into how technological advances are enabling new discoveries about brain function and creating new therapeutic possibilities.
The collaboration between leading experts in the field demonstrates the interdisciplinary nature of modern neurotechnology and highlights the potential for continued innovation in neural interface technologies.